Defining the stock market
The place where stocks are bought and sold is on a stock market. Every market has an index, which is a collection of equities chosen to represent the market's overall performance. For instance, the S&P 500 is a topic that frequently appears in the news. A 500-company index those trades on American markets makes up this index. It is believed that their success reflects the performance of the entire U.S. equities market. The majority of these businesses, including Microsoft, Walmart, Starbucks, and Amazon, are international in scope.
Defining an economy
The activities involved in producing and consuming money within an area or nation are collectively referred to as the economy. Changes in Gross Domestic Product are frequently used to gauge and follow the state of the economy in news (GDP). Other indicators of the health of the economy include expenditure, consumer confidence, the housing market, employment numbers, and consumer confidence.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total dollar amount of completed products and services produced in a nation over a given time period.
Understanding the relationship between the economy and the stock market
The stock market and the economy have never had a reliable relationship. Although they frequently move in roughly the same direction, the two frequently behave very differently, especially over shorter time periods. This atypical relationship has a number of causes. For instance:
1. The economy and the stock market have divergent outlooks
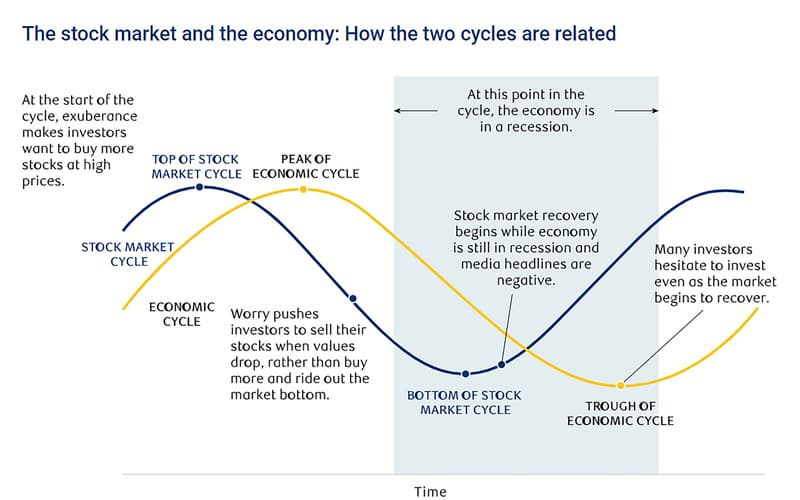
The stock market has an optimistic outlook. Based on how well you and other investors anticipate the firm performing in the future, you choose the price you are willing to pay for stock now. Some economic data, however, examine what has already occurred in the past. For instance, employment statistics display the number of persons who are unemployed and looking for work. Due to the fact that businesses frequently base their hiring and firing choices on the state of the economy, this statistic frequently lags behind the overall economy. As can be seen in the figure below, the stock market tends to be forward-looking, which causes it to frequently lead the economic cycle.
2. Disparities in geography make things more difficult in the partnership
On a country-by-country basis, we observe links between markets and economies changing. This is partially caused by the makeup of a nation's stock market.
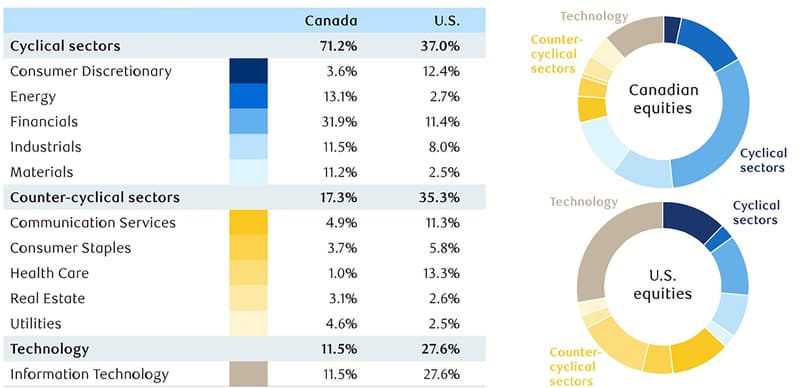
Take into account the distinctive features of both the Canadian and American equities markets. They have cyclical and countercyclical sectors that are vastly distinct from one another.
- Cyclical industries are those that are more inclined to follow the economy's trends. Stock values in cyclical sectors grow when the economy is doing well and customers are spending money. Their values drop when the economy isn't doing well. Energy and consumer discretionary are two examples.
- Typically, countercyclical industries produce necessities that people still need when money is tight. Because there is a constant demand for these goods and services, regardless of how the economy is performing, stocks in these industries fare well during economic downturns. Examples include consumer staples and utilities.
Key conclusions
- The TSX provides more exposure to classic cyclical sectors in Canada. Roughly two-thirds of the Canadian index is made up of the sectors Energy, Financials, Industrials, and Materials.
- Comparatively, the U.S. stock market (as measured by the S&P 500) is only about half as exposed to cyclical industries as the Canadian market. Its weight is significantly greater in countercyclical areas, though.
- The U.S. market also has a large influence on the information technology industry. A couple of the biggest corporations in the S&P 500 are Microsoft and Apple. These organizations tend to be less sensitive to the economy and are frequently able to avoid the difficulties that smaller businesses have because of their size, scale, business methods, and service offerings.
3. Investors' reactions to economic news are influenced by expectations
Good or terrible economic news is possible. But whether the news is better or worse than investors anticipated has a bigger impact on the markets. Think about these instances:
- Positive news on employment figures and the unemployment rate might increase investor confidence that the economy is expanding more quickly than anticipated.
- Investors are also encouraged by indications of higher-than-expected consumer activity. This is due to the fact that consumer spending fuels economic activity in the industrialized world. The earnings potential of publicly traded corporations is thereafter supported by this.
- A little bad news occasionally helps the markets. Say, for instance, that unexpectedly low employment numbers occur. This could raise market expectations that governments and central banks will implement monetary and fiscal measures to support economic growth. Investors should generally be encouraged by forecasts of increased stimulus (and hence increased expenditure) in the future.
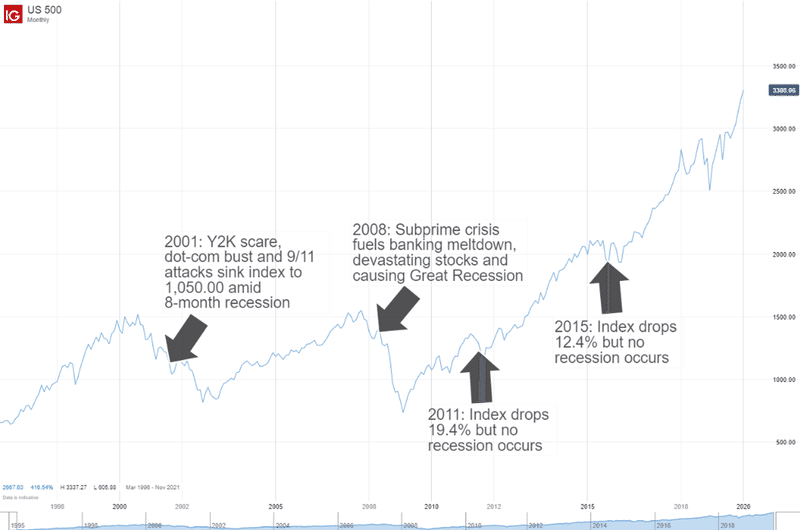
Some investors react by leaving the markets and looking for protection in cash when economic news is worse than anticipated. But historical evidence suggests that this frequently results in lost opportunities. When the outlook for the economy is bleak, stocks are frequently cheaper, which presents possibilities for investors willing to look ahead. The ideal way to make these choices is within the framework of a well-thought-out financial strategy.
How does the stock market affect the GDP?
We must first examine what propels economic growth in order to ascertain how the markets affect GDP. Spending and investment are the main drivers of the GDP of the US economy. A percentage growth rate of GDP is frequently displayed from one period to the next.
For instance, if the quarter-to-quarter growth rate is 2%, the annualized growth rate for the U.S. economy in that quarter was 2%. Here are a few of the important factors that contribute to GDP:
- The U.S. GDP is mostly driven by consumer spending.
- Spending by businesses involves hiring, investing in new technologies, purchasing new machinery and equipment, and constructing new offices and factories.
- Exports are purchases made by domestic businesses from clients abroad.
- Building roads, and bridges, and providing subsidies to various businesses, such as agriculture, are examples of government spending.
- Together, all of the aforementioned can be impacted by investors through the stock market, either badly or constructively.
How do bull markets affect the GDP?
When equity markets are increasing, we are in a bull market. The stock market largely has an impact on consumer confidence and financial conditions, which in turn affect GDP. Bull markets, in which stock prices are rising, are characterized by a large level of optimism about both the economy and the future prospects of different stocks.
Companies can utilize the money they raise by issuing new stock to grow their business, fund new initiatives, and hire more personnel. These activities all increase GDP. Since there is strong demand for stocks, it is simpler for businesses to issue new shares during a bull market.
The US GDP was $22.9 trillion in 2021. In 2022, it is anticipated to increase to $24.8 trillion.
These same businesses can also raise additional capital by borrowing from banks or issuing new debt, known as bonds if GDP is increasing—a sign that the economy is doing well. Investors buy the bonds, and the money is used for GDP-boosting corporate growth and expansion.
Investors and consumers are wealthier and more upbeat about prospects for the future as a result of growing stock prices. Improved spending as a result of this increased confidence may result in significant acquisitions like homes and cars. As a result, businesses experience increased sales and profits, which further boosts GDP.
How do bear markets affect the GDP?
In contrast, a bear market, which occurs when the stock market is down, results in dropping stock values and may be unfavorable to sentiment.
Investors hurry to sell stocks during a bear market in order to protect their investments from losses. Typically, the losses result in a decrease in consumer expenditure, especially if a recession is also being feared. Two consecutive quarters of negative—or contracting—GDP growth is frequently used to identify recessions.
When consumers start to cut back on their purchases, it can damage businesses' sales and income. Companies are consequently pressured to reduce expenses and staff. An increase in unemployment and more future uncertainty worsen the decline in consumer expenditure.
Additionally, finding new sources of funding for firms may prove tricky, and managing existing debt may become more onerous as income declines.
All of these elements contribute to a decline in consumer and company confidence, which results in less stock market investment. The declining investment and spending brought on by diminished confidence ultimately have a negative effect on GDP.
Economic volatility while investing in the stock market
In contrast, a bear market, which occurs when the stock market is down, results in dropping stock values and may be unfavorable to sentiment.
Investors hurry to sell stocks during a bear market in order to protect their investments from losses. Typically, the losses result in a decrease in consumer expenditure, especially if a recession is also being feared. Two consecutive quarters of negative—or contracting—GDP growth is frequently used to identify recessions.
When consumers start to cut back on their purchases, it can damage businesses' sales and income. Companies are consequently pressured to reduce expenses and staff. An increase in unemployment and more future uncertainty worsen the decline in consumer expenditure.
Additionally, finding new sources of funding for firms may prove tricky, and managing existing debt may become more onerous as income declines.
All of these elements contribute to a decline in consumer and company confidence, which results in less stock market investment. The declining investment and spending brought on by diminished confidence ultimately have a negative effect on GDP.
In conclusion
The stock market is a measure of economic sentiment that can affect gross domestic product (GDP). A healthy and expanding stock market is a sign that businesses are doing well and will keep doing so. This inspires confidence in customers, investors, and companies.
These organizations increase hiring, which lowers unemployment. They also borrow money, which has a number of beneficial effects. With more money and more people employed, more spending happens, strengthening the cycle and raising GDP. The opposite of what is described above happens when the stock market is performing poorly.
FAQ
What are the four different types of GDP?
There are four different sorts of GDP: real GDP, nominal GDP, actual GDP, and potential GDP, which is what GDP may be under perfect economic circumstances. Real GDP is GDP that has been corrected for inflation. Nominal GDP accounts for inflation.
Is the stock market measured by the GDP?
No, the stock market is not measured by GDP. GDP counts government spending, business investment, personal consumption, and net exports. However, given whether or not investors are enthusiastic about the future of the economy based on GDP data, the amount of GDP, particularly its growth or contraction, does have an impact on how the stock market performs.
Is GDP important?
GDP is significant because it tracks the success of many economic sectors, including consumption and investment, which are indicators of how well an economy is doing. A strong economy with increasing employment and business expansion is one with a growing GDP.
What are the special factors to consider?
Less is spoken about how the stock market affects GDP than how GDP affects the stock market. Corporate profits rise in response to rising GDP, which is positive for stocks.
The stock market affects GDP and the economy overall, albeit indirectly, whether there is a bull market or a bear market. The inverse happens when GDP declines, which results in less spending by businesses and consumers, which pushes the markets lower.
How do you build a portfolio that withstands all market conditions?
Understanding how the stock market and economy interact can assist you as an investor process economic news and maintaining your long-term perspective. In order to reduce the risks brought on by the ups and downs of economic and market cycles, it is crucial to diversify your portfolio over a variety of asset types. This might assist you to avoid the frequent mistakes investors make and make it simpler to stay the course through all market situations.






